
Back Anexo:Autopistas Interestatales Primarias Spanish Liste des interstates auxiliaires French List of auxiliary Interstate Highways SIMPLE Danh sách xa lộ liên tiểu bang phụ VI 美國州際公路輔助線列表 Chinese
| Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways | |
|---|---|
Highway shield for Interstate 295 | |
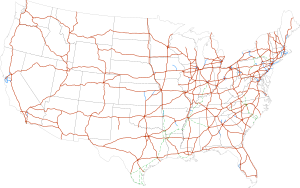 Interstate Highways in the 48 contiguous states | |
| System information | |
| Formed | June 29, 1956[1] |
| Highway names | |
| Interstates | Interstate X (I-X) |
| System links | |
Auxiliary Interstate Highways (also called three-digit Interstate Highways) are a subset of highways within the United States' Interstate Highway System. The 323 auxiliary routes generally fall into three types: spur routes, which connect to or intersect the parent route at one end; bypasses, which connect to the parent route at both ends; and beltways, which form a circle that intersects the parent route at two locations. Some routes connect to the parent route at one end but to another route at the other end; some states treat these as spurs while others treat them as bypasses. Like the primary Interstate Highways, auxiliary highways meet Interstate Highway standards (with rare exceptions).
The shorter auxiliary routes branch from primary routes; their numbers are based on the parent route's number. All of the supplement routes for Interstate 95 (I-95) are designated with a three-digit number ending in "95": I-x95. With some exceptions, spur routes are numbered with an odd hundreds digit (such as I-395), while bypasses and beltways are numbered with an even hundreds digit (such as I-695). Because longer Interstates may have many such supplemental routes, the numbers can repeat from state to state along their route, but they will not repeat within a state.
There are three states that have no auxiliary Interstate Highways: Alaska, Arizona, and New Mexico. North Dakota has an auxiliary route, but it is unsigned, and Wyoming's does not meet Interstate Highway standards.
- ^ Weingroff, Richard F. (Summer 1996). "Federal-Aid Highway Act of 1956, Creating the Interstate System". Public Roads. 60 (1). Washington, DC: Federal Highway Administration. Retrieved March 16, 2012.
