
Back نظام شبه رئاسي Arabic نظام شبه رئاسي ARZ Sistema semipresidencialista AST Yarı prezident respublikası AZ Зьмяшаная рэспубліка BE-X-OLD Полупрезидентска република Bulgarian অর্ধ-রাষ্ট্রপতিশাসিত শাসনব্যবস্থা Bengali/Bangla Sistema semipresidencialista Catalan Poloprezidentská republika Czech Semipräsidentielles Regierungssystem German
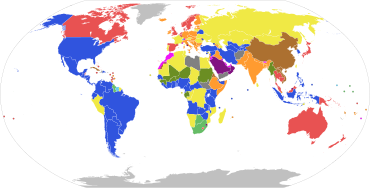
Parliamentary systems: Head of government is elected by and is accountable to the legislature
Presidential system: President is the head of government and is independent of the legislature
Hybrid systems:
Note: this chart represent de jure systems of government, not the de facto degree of democracy.[citation needed]
| Part of the Politics series |
| Politics |
|---|
|
|
| Part of the Politics series on |
| Executive government |
|---|
| Head of state |
| Government |
|
| Systems |
| Lists |
| Politics portal |
A semi-presidential republic, or dual executive republic, is a republic in which a president exists alongside a prime minister and a cabinet, with the latter two being responsible to the legislature of the state. It differs from a parliamentary republic in that it has an executive president independent of the legislature; and from the presidential system in that the cabinet, although named by the president, is responsible to the legislature, which may force the cabinet to resign through a motion of no confidence.[1][2][3][4]
While the Weimar Republic (1919–1933) and Finland (from 1919 to 2000) exemplified early semi-presidential systems, the term "semi-presidential" was first introduced in 1959 in an article by journalist Hubert Beuve-Méry,[5] and popularized by a 1978 work written by political scientist Maurice Duverger,[6] both of whom intended to describe the French Fifth Republic (established in 1958).[1][2][3][4]
- ^ a b Duverger (1980). "A New Political System Model: Semi-Presidential Government". European Journal of Political Research (quarterly). 8 (2): 165–187. doi:10.1111/j.1475-6765.1980.tb00569.x.
The concept of a semi-presidential form of government, as used here, is defined only by the content of the constitution. A political regime is considered as semi-presidential if the constitution which established it, combines three elements: (1) the president of the republic is elected by universal suffrage, (2) he possesses quite considerable powers; (3) he has opposite him, however, a prime minister and ministers who possess executive and governmental power and can stay in office only if the parliament does not show its opposition to them.
- ^ a b Veser, Ernst [in German] (1997). "Semi-Presidentialism-Duverger's concept: A New Political System Model" (PDF). Journal for Humanities and Social Sciences. 11 (1): 39–60. Retrieved 21 August 2016.
- ^ a b Duverger, Maurice (September 1996). "Les monarchies républicaines" [The Republican Monarchies] (PDF). Pouvoirs, revue française d'études constitutionnelles et politiques (in French). No. 78. Paris: Éditions du Seuil. pp. 107–120. ISBN 2-02-030123-7. ISSN 0152-0768. OCLC 909782158. Retrieved 10 September 2016.
- ^ a b Bahro, Horst; Bayerlein, Bernhard H.; Veser, Ernst [in German] (October 1998). "Duverger's concept: Semi-presidential government revisited". European Journal of Political Research (quarterly). 34 (2): 201–224. doi:10.1111/1475-6765.00405. S2CID 153349701.
The conventional analysis of government in democratic countries by political science and constitutional law starts from the traditional types of presidentialism and parliamentarism. There is, however, a general consensus that governments in the various countries work quite differently. This is why some authors have inserted distinctive features into their analytical approaches, at the same time maintaining the general dichotomy. Maurice Duverger, trying to explain the French Fifth Republic, found that this dichotomy was not adequate for this purpose. He therefore resorted to the concept of 'semi-presidential government': The characteristics of the concept are (Duverger 1974: 122, 1978: 28, 1980: 166):
1. the president of the republic is elected by universal suffrage,
2. he possesses quite considerable powers and
3. he has opposite him a prime minister who possesses executive and governmental powers and can stay in office only if parliament does not express its opposition to him. - ^ Le Monde, 8 January 1959.
- ^ Duverger, Maurice (1978). Échec au roi. Paris: A. Michel. ISBN 9782226005809.