
Back تلف الدماغ Arabic Mancadura cerebral AST Lesió cerebral Catalan Hjerneskade Danish Hirnschaden German Lesión cerebral Spanish Ajukahjustus ET Garun-lesio EU آسیب مغز FA Aivovaurio Finnish
This article needs more reliable medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources. (January 2019) |  |
| Brain damage | |
|---|---|
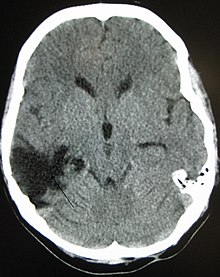 | |
| A CT of the head years after a traumatic brain injury showing an empty space where the damage occurred, marked by the arrow |
Neurotrauma, brain damage or brain injury (BI) is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors. In general, brain damage refers to significant, undiscriminating trauma-induced damage.
A common category with the greatest number of injuries is traumatic brain injury (TBI) following physical trauma or head injury from an outside source, and the term acquired brain injury (ABI) is used in appropriate circles to differentiate brain injuries occurring after birth from injury, from a genetic disorder (GBI), or from a congenital disorder (CBI).[1] Primary and secondary brain injuries identify the processes involved, while focal and diffuse brain injury describe the severity and localization.[citation needed]
Recent research has demonstrated that neuroplasticity, which allows the brain to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life, provides for rearrangement of its workings. This allows the brain to compensate for injury and disease.
- ^ "What is an Acquired Brain Injury?" (PDF). Headway. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-07-05. Retrieved 19 September 2016.